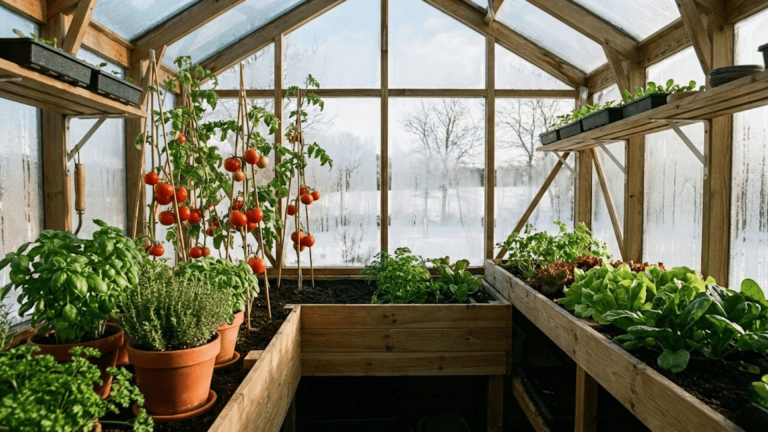
Step into your own glass sanctuary on a crisp morning, where tomatoes ripen in January, and herbs flourish while snow blankets the ground outside.
Greenhouse gardening opens up a world where seasons bend to your will, and growing limitations simply fade away.
You might be dreaming of extending your harvest, protecting seedlings, or creating a year-round growing paradise. A greenhouse becomes your personal climate control center, and getting started is more approachable than you think.
You’ll learn how to choose the right structure, keep temperatures just right, and understand what your plants crave.
Soon enough, that backyard dream becomes a thriving space that keeps producing long after traditional gardens have gone dormant.
Why Start a Greenhouse Garden?
Starting a greenhouse garden completely shifts what’s possible in your growing space.
You get an extended growing season that stretches well beyond summer, letting you harvest fresh produce even when frost covers the ground.
Your plants stay protected from unpredictable weather and hungry pests, which means fewer losses and less frustration.
The controlled environment gives you better yields and more consistent results since you’re managing temperature, humidity, and light exposure.
Beyond the practical perks, tending to a greenhouse offers mental health benefits. Nurturing plants in your climate-controlled haven provides grounding, especially during gray winter months when outdoor gardening is not an option.
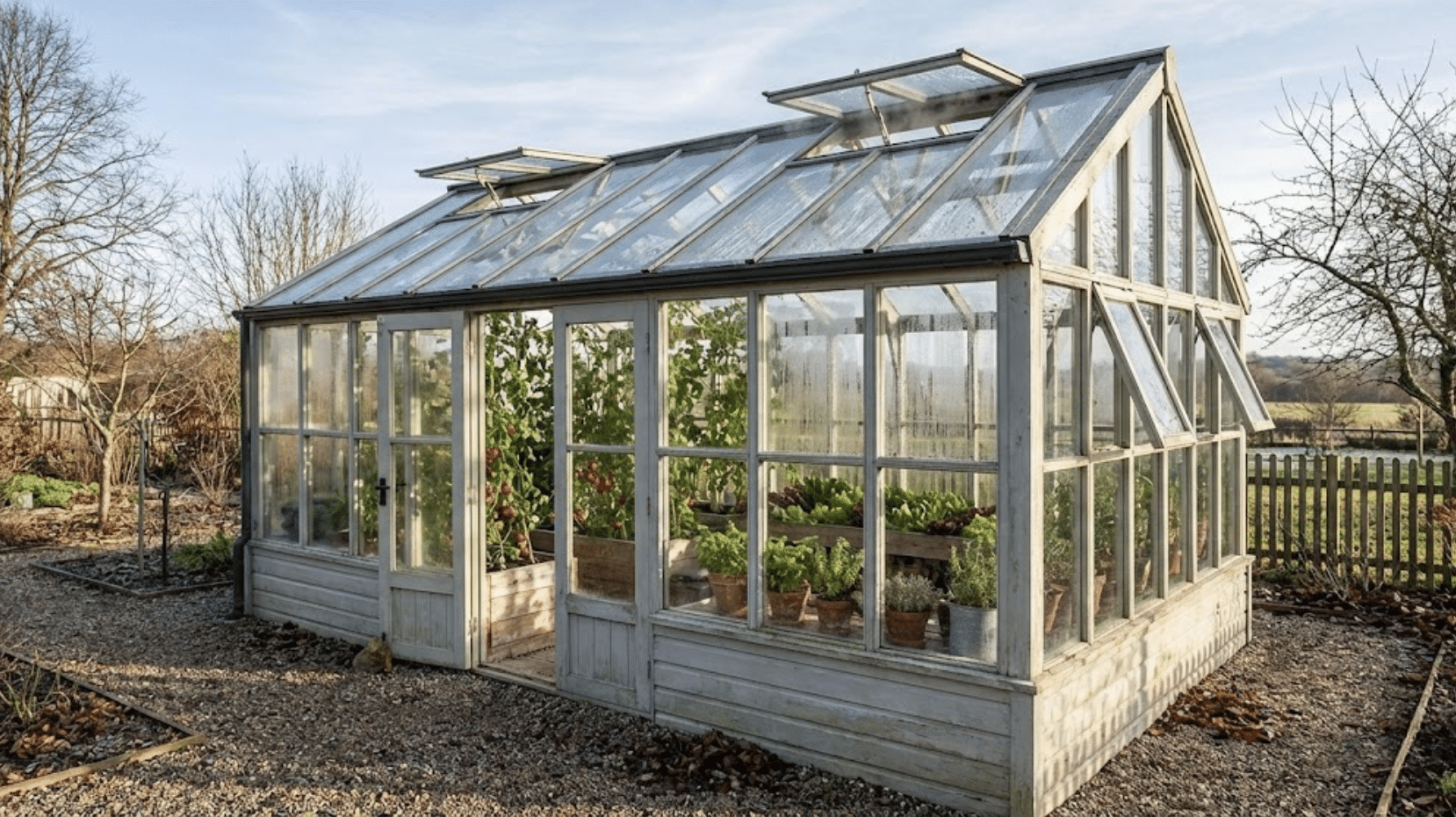
Choosing the Right Greenhouse
Your greenhouse choice sets the foundation for everything that follows. Getting the structure and placement right means smoother growing and fewer headaches down the road.
Types and Materials
Before you invest, understand what each option brings to your growing space.
| Material | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | Superior light, long-lasting | Heavy, breakable, pricey | Permanent setups |
| Polycarbonate | Great insulation, durable | Can yellow over time | Year-round growing |
| Plastic Film | Affordable, easy to replace | Shorter lifespan, tears | Beginners, seasonal use |
| Portable Structures | Easy to move, low cost | Less sturdy | Renters, trial runs |
| Permanent Structures | Durable, better control | Higher cost, may need permits | Long-term growers |
Location, Orientation, and Siting
Where you place your greenhouse matters just as much as what you build.
- Maximize sunlight exposure by positioning the longest side south-facing, aiming for at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sun daily.
- Shield from strong winds using natural windbreaks like fences, hedges, or existing buildings without blocking precious light.
- Keep water and power sources nearby, so you’re not dragging hoses across the yard or running extension cords every time you need them.
- Ensure easy access year-round with a clear path that won’t turn into a muddy mess during rainy seasons or get buried under snow.
Essential Greenhouse Setup
Once your structure is in place, the right tools and growing medium turn an empty shell into a productive space. These essentials keep your plants thriving and make daily maintenance feel less like work.
Tools and Equipment
You don’t need to buy everything at once, but certain tools make greenhouse life significantly easier.
- Thermometers and hygrometers for tracking temperature and humidity
- Timers and moisture meters for automated watering and lighting schedules
- Benches and shelving for maximizing vertical space
- Irrigation components like drip lines or soaker hoses
Soil, Containers, and Growing Medium
What your plants grow in matters just as much as the greenhouse itself.
- Start with high-quality potting mix rather than garden soil, which compacts in containers and drains poorly under glass.
- Raised beds offer more root space and better drainage, while containers give you flexibility to move plants around as seasons change.
- Add compost and organic matter regularly to keep soil structure loose, nutrient-rich, and teeming with beneficial microbes.
- Healthy soil means resilient plants that resist pests and diseases naturally, reducing your need for interventions down the line.
Climate Control and Environmental Management

Your greenhouse only works as well as the environment inside it. Nailing temperature, airflow, and humidity keeps plants healthy and prevents the common pitfalls that frustrate new growers.
1. Temperature Regulation
Most plants thrive between 65 and 75 degrees during the day, dropping about 10 degrees at night. Cold months may need a heater or heat mats for seedlings; summer heat requires shade cloth, ventilation, or evaporative cooling.
Monitoring daily fluctuations helps you catch problems early before plants start wilting or bolting unexpectedly.
2. Ventilation and Airflow
Fresh air prevents disease and keeps temperatures from spiking on sunny days. Roof vents, side vents, and open doors create natural cross-breezes, while small fans boost circulation in tight corners.
Automatic vent openers respond to temperature changes without you lifting a finger, making climate management hands-off even when you’re away for the day.
3. Humidity and Moisture Management
Balanced humidity sits around 50 to 70 percent for most crops, though some prefer it drier or more tropical. Too much moisture invites mold, mildew, and fungal diseases that spread fast in enclosed spaces.
Good airflow, strategic watering times, and occasional venting keep humidity in check without drying out your plants completely.
Watering and Irrigation Best Practices
Watering seems simple until you realize greenhouse plants need a completely different approach than outdoor beds.
Too much leads to root rot, too little stresses your plants, and finding that sweet spot takes some attention.
- Water early in the morning so foliage dries before nightfall, reducing fungal disease risks.
- Check soil moisture 2 inches deep rather than relying on surface dryness, which can be misleading.
- Install drip systems or soaker hoses to deliver water directly to roots and minimize waste.
- Use moisture sensors to take the guesswork out of when your plants actually need a drink.
- Ensure proper drainage in all containers so excess water escapes instead of pooling around roots.
Getting your watering rhythm dialed in makes everything else easier. Your plants will tell you when you’ve got it right through steady growth and vibrant leaves.
Choosing Plants for Beginners
Starting with the right plants builds your confidence and delivers quick rewards. Some crops practically grow themselves in a greenhouse, making them perfect for your first season.
Easy Vegetables and Greens
These reliable performers give you fresh harvests without demanding expert-level care.
| Plant | Why It Works | Harvest Time |
|---|---|---|
| Lettuce | Grows fast, tolerates cooler temps | 30-45 days |
| Spinach | Cold-hardy, multiple cuttings | 40-50 days |
| Kale | Extremely forgiving, productive | 50-65 days |
| Tomatoes | Thrives in warmth, heavy yields | 60-85 days |
| Peppers | Loves greenhouse heat, long season | 70-90 days |
| Cucumbers | Fast grower, vertical training saves space | 50-70 days |
Herbs and Specialty Crops
Quick-growing herbs and microgreens offer nearly instant gratification for impatient growers.
| Plant | Why It Works | Harvest Time |
|---|---|---|
| Basil | Warm-weather lover, continuous harvest | 3-4 weeks |
| Mint | Nearly indestructible, spreads easily | 4-6 weeks |
| Cilantro | Cool-season favorite, bolt-resistant indoors | 3-4 weeks |
| Microgreens | Ultra-fast, nutrient-dense, minimal space | 7-14 days |
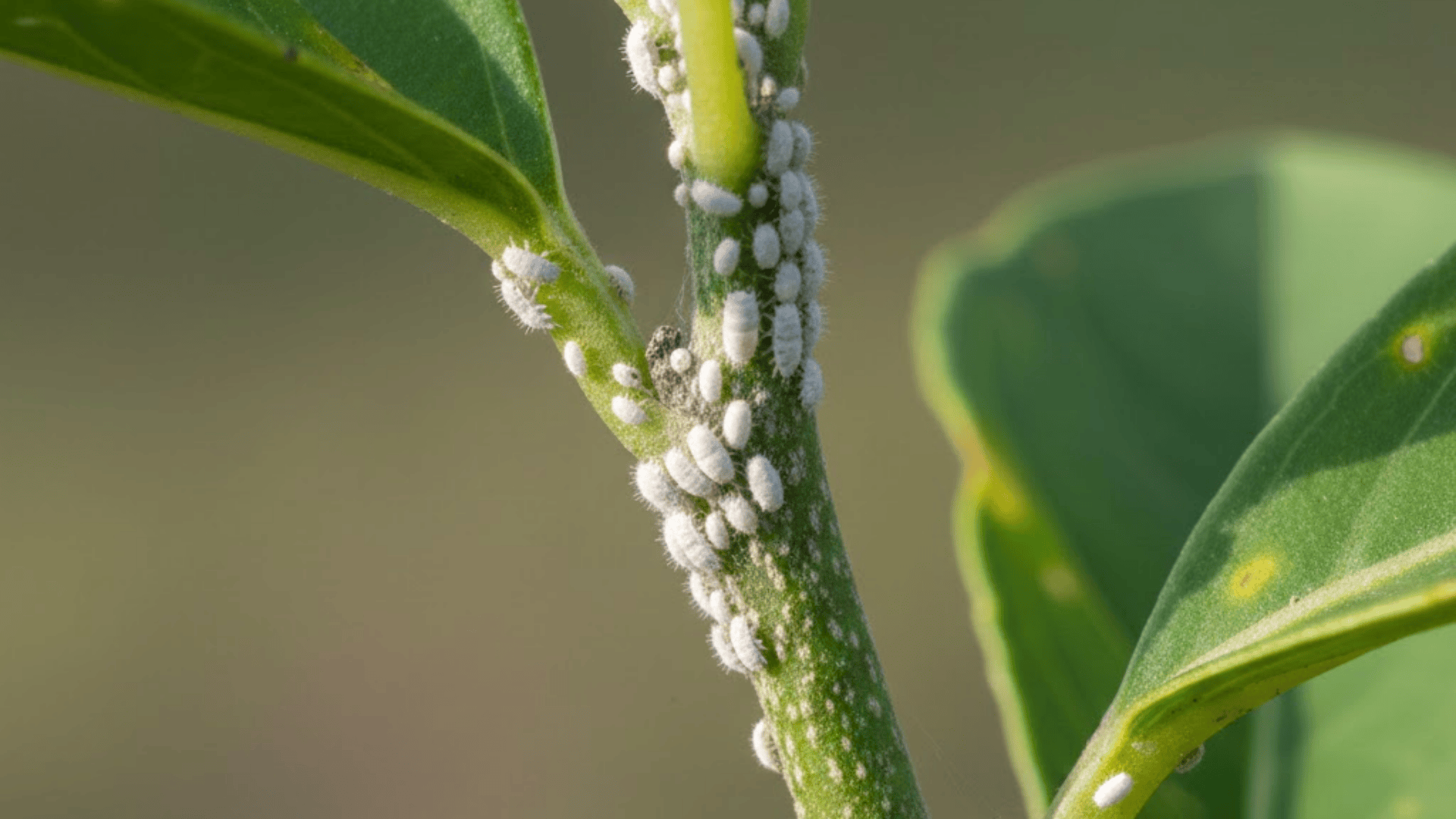
Pest and Disease Prevention for Greenhouse Gardens
Greenhouses create ideal conditions for plants, but pests love the warmth and humidity, too.
Aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites are the usual suspects, often hiding under leaves or near growing tips. Catch them early by inspecting plants weekly, especially new growth and leaf undersides.
Beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings handle infestations naturally without chemicals, while yellow sticky traps monitor and catch flying pests.
Keep your space clean by removing dead leaves, sanitizing tools, and avoiding overwatering, which invites fungal problems.
A tidy greenhouse with good airflow stops most issues before they spiral out of control.
Year-Round Maintenance and Seasonal Care
Keeping your greenhouse productive means adjusting your approach as seasons shift. Regular upkeep prevents small issues from becoming expensive repairs.
| Task | When | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Clean glass or panels | Spring and fall | Restores light transmission up to 30% |
| Rotate crops | Every planting cycle | Balances soil nutrients and disrupts pest lifecycles |
| Add insulation or bubble wrap | Late fall | Reduces heat loss and lowers energy costs |
| Install shade cloth | Early summer | Lowers interior temps 10-15°F and prevents sunscald |
| Check seals and caulking | Before winter | Eliminates drafts that cause temperature fluctuations |
| Disinfect benches and tools | Between seasons | Removes pathogens and fungal spores |
Advanced Tips for Future Growth
Once you’ve mastered the basics, your greenhouse becomes a testing ground for techniques that boost yields and maximize every inch of space.
Pushing boundaries keeps the learning curve exciting and your harvests impressive.
- Train vining crops vertically using trellises, strings, or cages to free up floor space and improve air circulation around plants.
- Add grow lights during the winter months to extend daylight hours and keep photosynthesis strong when natural light dwindles.
- Experiment with hydroponics or aquaponics for faster growth rates and higher yields in smaller footprints.
- Layer planting heights by using tiered shelving or hanging baskets to triple your growing capacity without expanding your greenhouse.
- Try succession planting by starting new crops every few weeks so harvests keep rolling in rather than arriving all at once.
These techniques aren’t just for commercial growers. Once you see how much more your greenhouse can handle, you’ll wonder why you didn’t start experimenting sooner.
The Bottom Line
Your greenhouse starts with a single seed and grows into something far more rewarding than you might expect right now.
These greenhouse gardening tips give you the foundation to avoid common mistakes and build confidence with every harvest. You’ll learn through trial, adjust as seasons change, and figure out what works best in your unique space.
Soon enough, you’ll be the one sharing advice with curious neighbors peering through the glass.
What plants are you most excited to grow first? Drop a comment below and let’s swap ideas about turning your greenhouse dreams into a thriving reality.