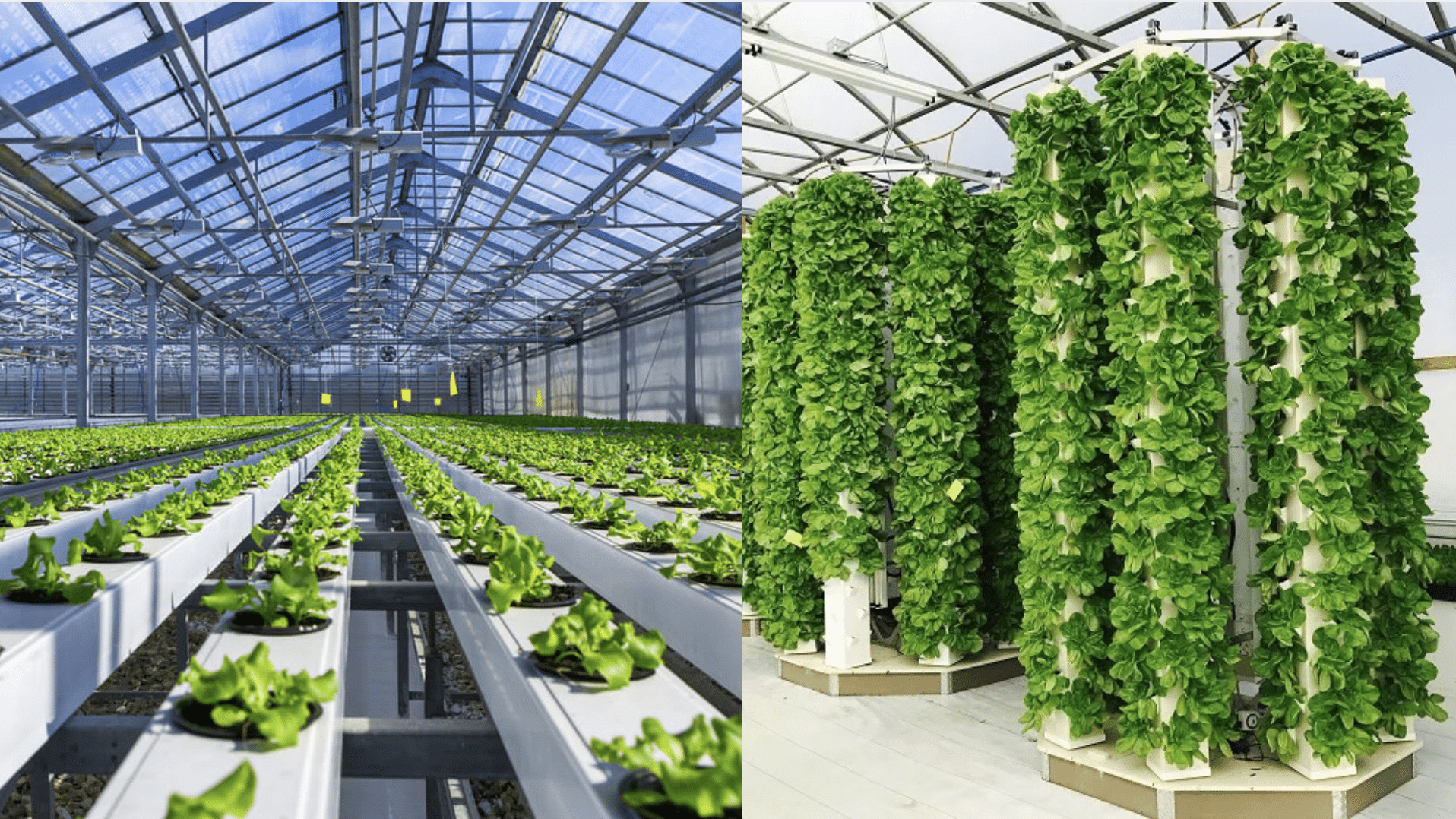
Imagine growing plants without using any dirt! That’s what aeroponics and hydroponics do: they help plants grow in the air or water, not soil.
These two innovative methods are transforming the way we grow food, particularly in urban areas where space for traditional farms is limited.
In aeroponics, plants hang in the air, and their roots get sprayed with water and nutrients. In hydroponics, plants’ roots are submerged in water that contains everything they need to grow.
These methods are great because they use less water than traditional farming, and you can grow a lot of food in small spaces, like on rooftops or in empty buildings.
Both aeroponics and hydroponics are super important for the future of farming.
In this blog, I’ll explain the difference between aeroponics and hydroponics, two innovative methods for growing plants without soil.
What Is Aeroponics?
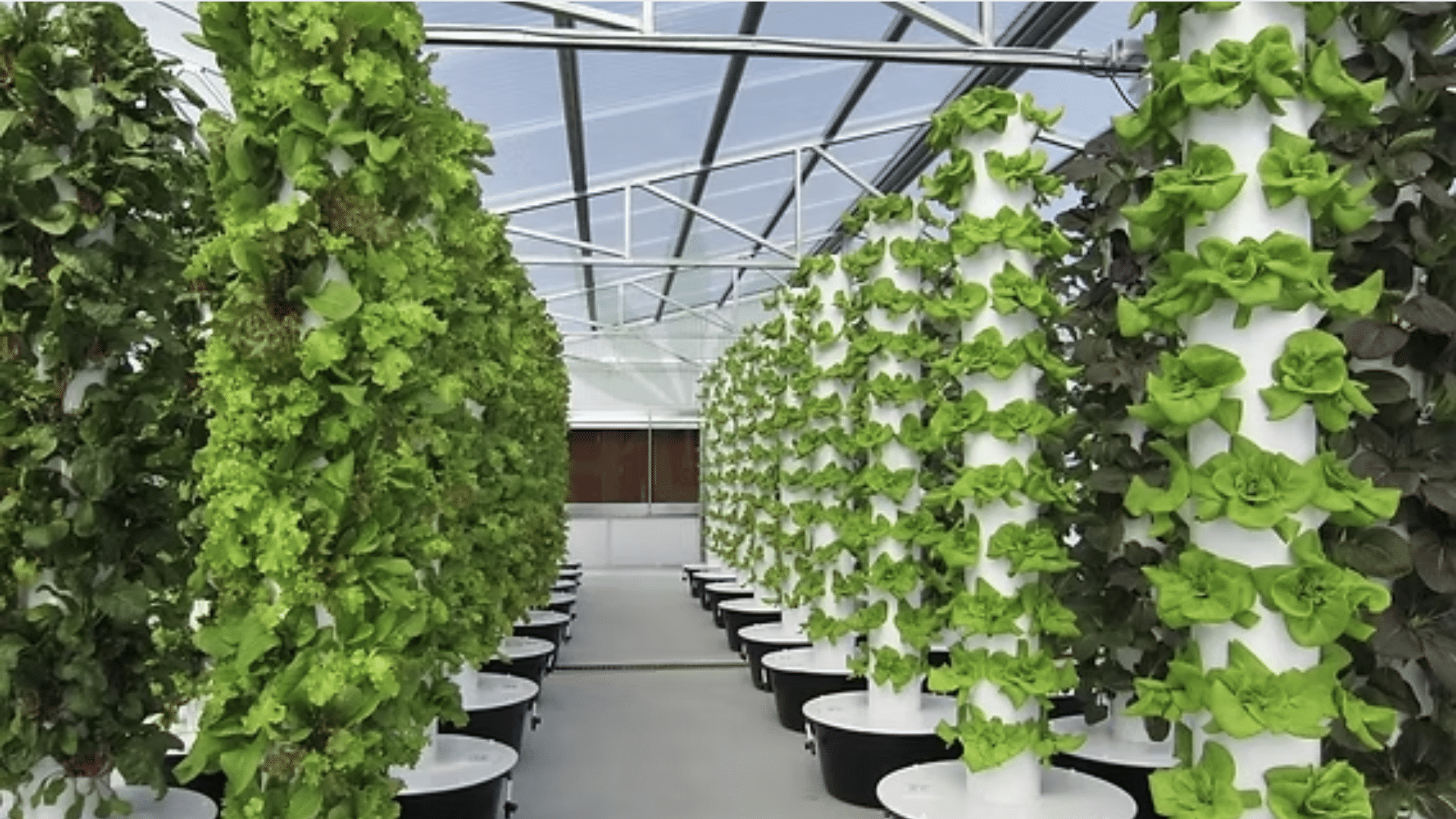

Aeroponics is a way of growing plants without soil by suspending their roots in the air and providing them with a fine mist of water and nutrients.
This method allows the roots to get plenty of oxygen and nutrients directly, which can help plants grow faster and healthier.
In aeroponics, plants are placed in special chambers where their roots are exposed to the air.
A misting system sprays a nutrient-rich solution onto the roots, providing water and nutrients. Since the roots are in the air, they get a lot of oxygen, which speeds up growth.
Components of Aeroponics
- Misting Systems: These systems deliver a fine mist of water and nutrients directly to the plant roots. This ensures the roots get everything they need, including water and essential nutrients, without being submerged.
- Root Chambers: These are the areas where plant roots hang freely in the air. The roots are exposed to the mist and the air, allowing them to absorb nutrients efficiently.
- Environmental Controls: These are systems that regulate the growing conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light. By adjusting these factors, environmental controls ensure that the plants get healthy, rapid growth.
- Root Chambers: These are the areas where plant roots hang freely in the air. The roots are exposed to the mist and the air, allowing them to absorb nutrients efficiently while getting plenty of oxygen for faster growth.
What Is Hydroponics?
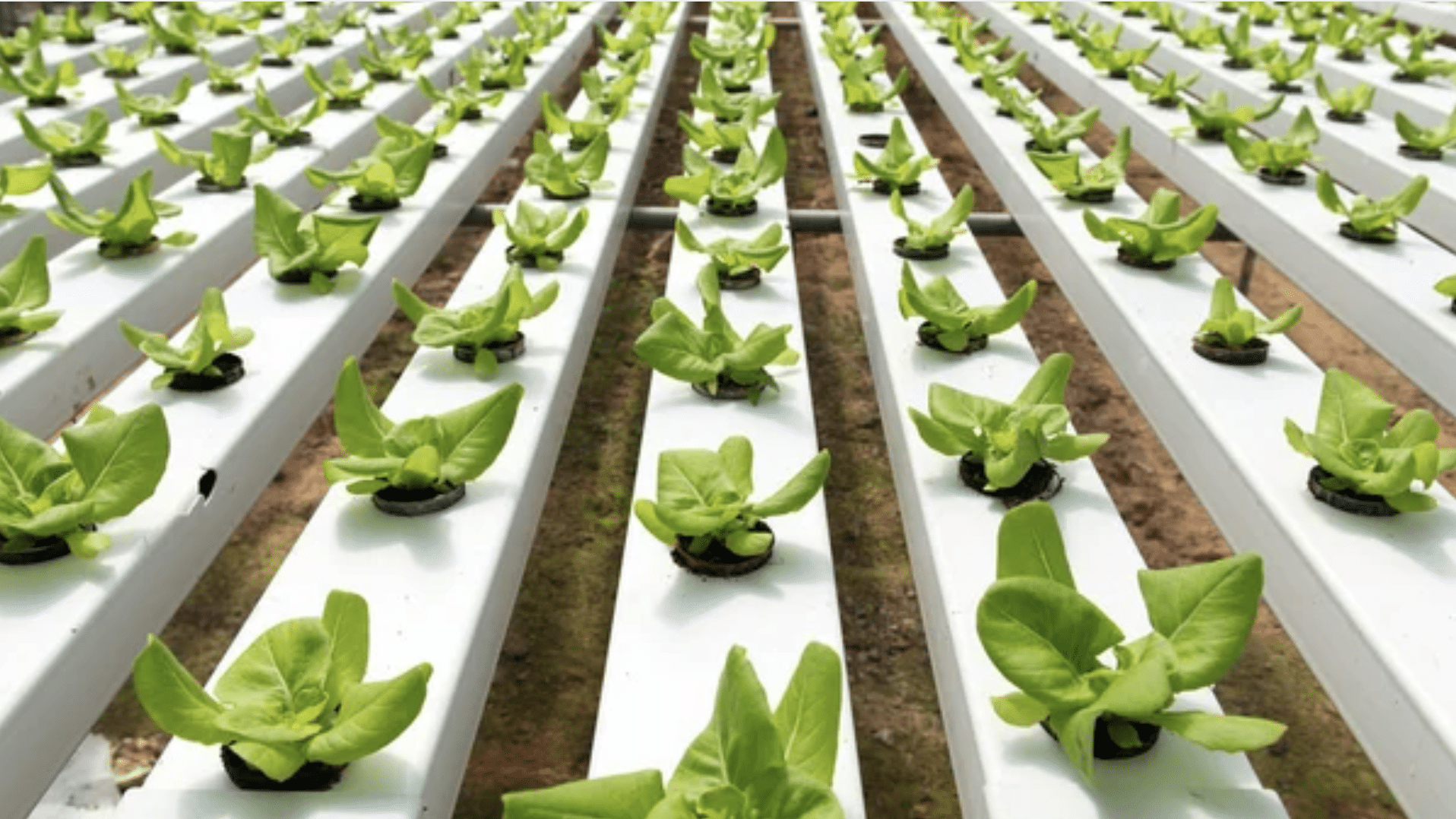

Hydroponics is another method of growing plants without soil, but instead of air, plants grow in water.
The roots of the plants are submerged in a nutrient-rich solution, which provides everything they need to grow.
In hydroponics, plants are placed in a water-based solution that contains all the essential nutrients they need.
The plant roots are either submerged in the water or sit in a grow medium that holds the water and nutrients. The system continuously or periodically circulates water to ensure the roots stay nourished.
Components of Hydroponics
- Growing Mediums: In hydroponics, plants still require a medium to support their roots, but instead of soil, we use specialized materials such as perlite, coconut coir, or clay pellets. These media help keep the roots stable while letting water and nutrients flow easily to them.
- pH and EC Meters: These tools measure the water’s pH level (indicating its acidity or alkalinity) and the EC (which indicates the water’s nutritional content). Maintaining these levels accurately is crucial for healthy plant growth.
- Water Pumps and Tubing: Water pumps push the nutrient solution from the reservoir through the system to the plants. The water is often distributed through tubes or pipes that direct it to each plant, ensuring consistent delivery of nutrients.
- Drip Systems or Flood-and-Drain Mechanisms: Some hydroponic systems use a drip system, where water is delivered drop by drop to the roots. Others use a flood-and-drain system, where the tray fills with water and then drains away.
Key Differences Between Aeroponics and Hydroponics
If you’re considering soilless gardening, you’ve likely heard of aeroponics and hydroponics. Both methods help plants grow without soil, but they work in different ways.
| Aspect | Aeroponics | Hydroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Growing Medium | Roots suspended in air/mist | Roots submerged in water or media |
| Water Usage | Uses less water | Uses a steady supply of water |
| Plant Support | Roots hang freely in the air | Roots are supported by water or a growing medium |
| Cost and Setup | Higher initial equipment costs, complex setup | Lower setup cost, easier to maintain |
| Efficiency | Faster growth, energy-efficient, space-saving | Steady growth, more water usage, space-efficient |
Aeroponics: Pros and Cons Explained
Aeroponics offers an innovative way to grow plants without soil, but like any system, it comes with its own set of advantages and challenges.
Pros
- Maximum Water and Nutrient Efficiency: Aeroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional gardening, making it highly efficient and environmentally friendly. The plant roots receive nutrients through a mist, which reduces waste and promotes better plant growth.
- Higher Oxygen Availability for Roots: Since the roots are suspended in air, they can take in more oxygen, which helps the plants grow faster and become stronger overall. This leads to quicker harvests and bigger yields.
Cons
- High Initial Setup Cost: The technology behind aeroponics can be expensive, especially for larger systems. This includes purchasing equipment like misting systems, root chambers, and environmental control systems.
- Technical Complexity: Aeroponics systems demand close attention and precise control of factors like temperature, humidity, misting cycles, and nutrient levels. For beginners, this can be challenging and require a steep learning curve.
- Need for Constant Monitoring: Since the roots are suspended in air, they can take in more oxygen, which helps the plants grow faster, develop healthier roots, and become stronger overall. This leads to quicker harvests and bigger yields.
Hydroponics: Pros and Cons Explained
Hydroponics offers a soil-free way to grow plants efficiently, but like any system, it has its benefits and challenges.
Pros
- Easier to Set Up and Maintain: Hydroponics systems are generally more straightforward to set up and maintain, especially for beginners.
- More Forgiving for Beginners: It’s easier to adjust nutrient levels and water flow, making it a good choice for newcomers to soil-free gardening.
- Less Risk of Pests and Diseases: With no soil, there is a lower risk of pests and soil-borne diseases, making it easier to manage plant health.
- Versatility in Location: Hydroponic systems can be set up indoors or outdoors, providing flexibility in location and environmental control.
Cons
- Higher Water Usage: While still more efficient than traditional soil farming, hydroponics requires a steady supply of water, which can be less efficient than aeroponics.
- Potential for Root Diseases: If the water is not properly managed or cleaned, there is a higher risk of diseases affecting plant roots.
- Initial Setup Cost: The equipment and supplies required for hydroponics can be costly, especially for larger setups or advanced systems.
- Nutrient Imbalance: If nutrient levels aren’t carefully monitored, plants can suffer from deficiencies or toxicity, affecting growth and health.
- Energy Consumption: Some hydroponic systems, especially those with pumps and lights, may require a significant amount of energy to operate.
Which System is Better for You?
Choosing between aeroponics and hydroponics depends on your space, experience, and the type of plants you want to grow.
Ideal Conditions for Aeroponics
Aeroponics is great if you have limited space, like on a small rooftop or in a small room.
It’s perfect for people who have experience with gardening and know how to take care of plants carefully.
This system helps plants grow faster and healthier, but it needs a lot of attention to make sure everything is just right.
Ideal Conditions for Hydroponics
Hydroponics works well if you’re just starting out with gardening or want to grow a lot of plants. It’s easier to set up and take care of than aeroponics.
Hydroponics is also good for bigger spaces, like greenhouses, where you can grow many plants at once.
If you want to grow plants without a lot of fuss, hydroponics is a good choice.
Conclusion
I’ve found that aeroponics delivers nutrients through a mist, allowing for faster growth, healthier roots, and better oxygen absorption.
It uses up to 90% less water compared to traditional gardening, which makes it highly sustainable.
On the other hand, hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water to nourish plants, and it’s easier to set up and maintain, making it a great choice for beginners.
Aeroponics is perfect for those with limited space and who want maximum efficiency, but it can be more complex and expensive.
Hydroponics is easier to set up and maintain, making it ideal for beginners.
By considering what works best for you, I’m sure you’ll find the system that fits your needs and goals.