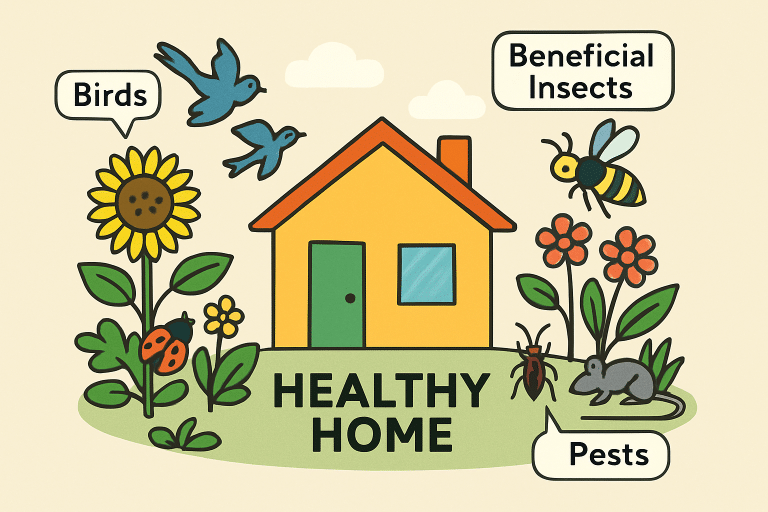
Sustainable pest control aims to protect homes while preserving local biodiversity. More homeowners are choosing eco-friendly solutions that are safe for families, provide lasting results, and reduce risks to beneficial wildlife and pollinators. Environmentally conscious pest management not only protects property but also contributes to healthier ecosystems and communities.
For residents in Citrus County seeking these approaches or needing solutions for current infestations, options like pest control Inverness, FL, offer environmentally responsible interventions.
Today’s pest management emphasizes a careful balance between human health, comfort, and sustainability. It involves identifying the root causes of infestations—whether seasonal or persistent—and applying consistent preventive measures. By targeting the environmental factors that attract pests, control strategies move from reactive treatments to proactive care, safeguarding families, pets, and beneficial organisms while supporting long-term, holistic solutions.
What Drives Pest Invasions?
Pest activity is not random but is driven by environmental cues, shifts in weather, and human habits. Sudden changes in season, particularly as temperatures drop, can force pests indoors in search of warmth, protection, and new food sources. Damp, humid conditions often result in a spike of insects such as silverfish or cockroaches, while drought can prompt rodents to seek moisture within homes.
Even small crumbs or a leaky faucet can unlock the door for persistent pest problems. Construction or landscaping changes can inadvertently disrupt pest habitats, sending populations scurrying toward the nearest shelter—often a residential property. An understanding of these factors enables proactive pest deterrence rather than reactive treatment, allowing homeowners to break the cycle before it becomes established.
How Indoor Environments Attract Pests
Even a well-maintained house can unknowingly harbor pests if certain risk factors are overlooked. Leaving food exposed on counters, neglecting trash bins, and overlooking leaks all act as magnets for rodents and insects, which have highly sensitive senses that enable them to track down food and water.
Cluttered attics, garages, and basement spaces offer perfect nesting grounds, providing the shelter and quiet pests need to reproduce undetected. Leaky plumbing provides a continual water supply that attracts ants and cockroaches, which can survive without food far longer than without water, while gaps around windows and doors serve as easy entry points for spiders, centipedes, and mice.
Even minor oversights, such as damp areas or unsealed cracks, can make a home highly appealing to unwanted visitors, as highlighted by sources like Southern Living, which detail common household features that attract pests. Inside walls or behind appliances, even a few unnoticed crumbs or a steady drip can make the difference between a pest-free home and a sudden infestation. Understanding how seemingly harmless habits or minor repairs can have a significant impact is crucial for reducing the risk of an outbreak.
Understanding Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is the gold standard for safe and sustainable pest control. Rather than relying on heavy chemical interventions, IPM employs a stepwise process involving identification, monitoring, and a strategic combination of physical, biological, and minimal chemical controls.
Careful observation allows for targeted responses—by understanding which pests are present and why, broad-spectrum solutions can often be avoided in favor of measures that minimize risk to humans and non-target species. In the IPM framework, education is as vital as intervention, empowering residents to identify and resolve potential problems independently.
Chemical vs. Natural Solutions
The debate between chemical and natural pest management boils down to striking a balance between immediate effectiveness and long-term safety. Chemical sprays may offer quick relief by rapidly knocking down active infestations, but they can harm beneficial insects, pets, and human occupants. Additionally, residues often persist in living environments, posing chronic health risks.
Many commercial products, although potent, can also lead to resistance in pest populations, rendering control efforts less effective over time. Natural options, such as pheromone traps, essential oil repellents, or introducing ladybugs to control aphids, limit negative environmental impacts while sustaining effective control.
These tactics often support the natural balance, attracting beneficial organisms rather than indiscriminately eliminating all insects. The right choice often combines these strategies, using chemicals as a last resort when non-toxic measures fail or as part of a focused, limited application plan rather than a routine, broad use.
Impact on Local Ecosystems
Sustainable pest management looks beyond the home to the broader landscape. The indiscriminate use of pesticides can decimate pollinator populations and disrupt food chains, threatening birds, bats, and other natural predators of pests. For example, bees and butterflies are critical for pollinating food crops and native plants—yet are among the most vulnerable to pesticide drift and residue.
Allowing beneficial wildlife to thrive naturally can help mitigate pest issues and reduce long-term dependence on chemical solutions. At the same time, avoiding unnecessary chemical use protects water quality; runoff from yards and gardens often finds its way into local waterways, where it can impact aquatic life and drinking sources.
Taking a holistic approach to pest control supports long-term biodiversity and helps build a resilient, healthy ecosystem that can weather changes or pest outbreaks with less reliance on human intervention.
Preventing Pest Problems Proactively
- Store pantry staples in sealed, airtight containers to eliminate food attractants that might draw ants, rodents, or pantry moths.
- Declutter potential hiding places and keep storage spaces tidy to deter nesting and reproduction by pests like spiders, roaches, and mice.
- Install door sweeps, caulk holes, and seal utility line gaps to block entry, making it difficult for pests to find a way indoors.
- Dispose of garbage regularly, secure trash lids, and manage compost bins away from home foundations to prevent inviting scavengers and flies.
Preventive action serves as your first—and best—line of defense against infestations. Regular inspection and sanitation help catch small problems before they multiply into costly, difficult-to-control invasions. Many issues can be addressed with just a few simple, consistent habits, saving both time and expense in the long run. Catching leaks, repairing screens, and limiting moisture inside your property are equally important for discouraging persistent pests.
Educating Communities on Pest Control
Community engagement amplifies the success of sustainable pest management. Local workshops, informative newsletters, and neighborhood initiatives empower residents to recognize and address risks collectively, rather than leaving each household to fight infestations alone.
By sharing actionable tips, new research, and even stories of pest-free households, neighbors can support one another and build motivation for best practices. This culture of education ensures that preventative action becomes routine, not just a reaction to seeing pests. Proactive communities not only reduce individual home infestations but also limit the spread of pests across property boundaries, creating healthier, pest-resilient environments for all.
Future Trends in Pest Control
Pest control is poised for a technological revolution, from AI-powered monitoring systems to non-toxic lures and biological interference strategies that disrupt pest reproduction. Homeowners can now use smart sensors to detect pest movement or changes in population, allowing for precise interventions before infestations take hold.
As consumer preferences shift toward low-impact products and smarter, more sustainable tools, the reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides is expected to decline. Companies are also investing in the development of biodegradable, species-specific controls that drastically reduce unintended harm to beneficial insects and wildlife.
Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Pest Control for Homes and Ecosystem
Sustainable pest control represents a holistic approach that balances the protection of homes with the preservation of local ecosystems. By understanding the environmental and behavioral factors that drive pest invasions, homeowners can shift from reactive treatments to proactive prevention, minimizing risks to families, pets, and beneficial wildlife. Integrated Pest Management, combined with a thoughtful blend of natural and chemical solutions, enables effective control while minimizing environmental impact.
Beyond individual households, community education and engagement further strengthen pest resilience, promoting healthier neighborhoods and supporting biodiversity. As technology advances and eco-conscious methods continue to evolve, the future of pest control promises more precise, sustainable, and safe strategies that protect both property and the environment.